Ester and Alkyd Compounds
Properties
Alkyd resins are thermoplastic or thermosetting polyester resin compositions. They are known for their good weathering properties and are important ingredients in many synthetic paints due to their versatility and low cost. They are commonly produced by polycondensation of an alcohol (polyol) and a dicarboxylic acid or its anhydride. For instance, glycerol and phthalic anhydride react to form the polyester glyptal.
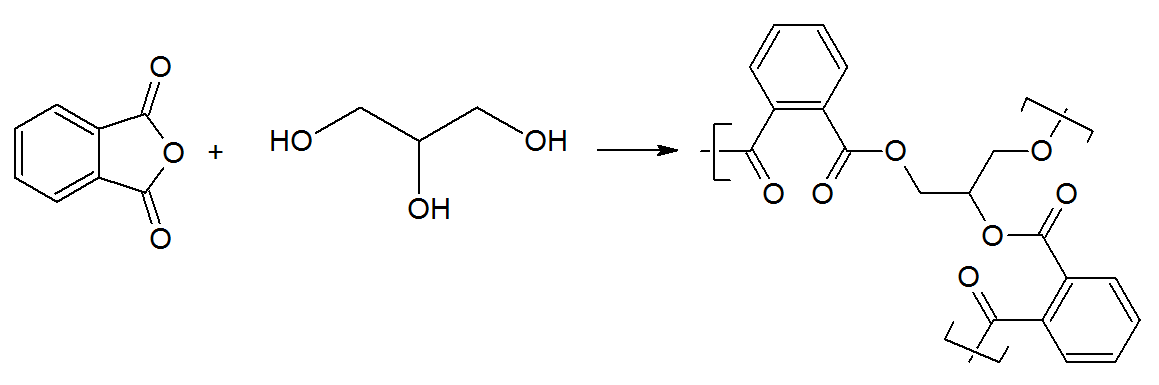
Often long fatty acids are co-reacted with the anhydride which improve the flexibility and the “drying” speed of the alkyd resin. The principal polybasic acids used in alkyd preparation include phthalic anhydride, isophthalic acid, maleic anhydride, and fumaric acid, among many others. The principal types of polyols used in alkyd synthesis are glycerol, trimethylolethane, trimethylolpropane, pentaerythritol, ethylene glycol, and neopentyl glycol. The overwhelming majority of the monobasic acids used in alkyd resins are long-chain fatty acids of natural occurrence. The selection of each of the aforementioned ingredients (polyols, mono-, and polyacids) affect the properties of the resin and may also affect the choice of manufacturing processes.
Applications
Alkyds are important ingredients in many synthetic paints, varnishes and enamels. The principal applications are furniture and architectural coatings, printing inks, special-purpose coatings and automotive refinishing primers. Alkyds are also used as thermosetting plastics that can be (compression or transfer) molded. They are sometimes used in molding electrical or electronic articles such as switches, housings, and various electronic components.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |